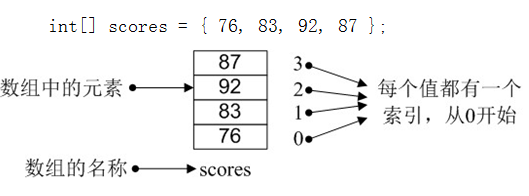
# 数组
int[] scores = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 }
System.out.println(scores[2]); // 3
1
2
2
# 声明数组
语法:
数据类型[ ] 数组名;
// 或者
数据类型 数组名[ ];
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
其中,数组名可以是任意合法的变量名,如:
// 存储学生成绩的数组,类型为整型
int[] scores;
// 存在身高的数组,类型为浮点型
double height[];
// 存储学生姓名的数组,类型为字符串
String[] names;
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 分配空间
简单地说,就是指定数组中最多可存储多少个元素
语法:
数组名 = new 数据类型 [ 数组长度 ];
1
其中,数组长度就是数组中能存放元素的个数,如:
scores = new int[5];
height = new double[5];
names = new String[5];
1
2
3
2
3
也可以将上面的两个步骤合并,在声明数组的同时为它分配空间
int[] scores = new int[5];
1
# 赋值
scores[0] = 100;
scores[1] = 99;
1
2
2
# 处理数组中数据
System.out.println(scores[1]); // 99
1
同时声明数组、分配空间和赋值:
int[] scores = {89, 90, 100, 78};
1
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个长度为5的字符串数组,保存考试科目信息
String[] subjects = new String[5];
// 分别为数组中的元素赋值
subjects[0] = "Oracle";
subjects[1] = "PHP";
subjects[2] = "Linux";
subjects[3] = "Java";
subjects[4] = "HTML";
System.out.println("数组中第4个科目为:" + subjects[3]);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
例子:
// error:
// Cannot define dimension expressions when an array initializer is provided
int[ ] score = new int[ 4 ] { 90, 12, 34, 77 };
// error:
// Variable must provide either dimension expressions
// or an array initializer
int[ ] score = new int[ ];
// right
int score[ ] = new int[ ] { 34, 90, 87, 54, 24 };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 循环操作
int[] arr = { 34, 53, 98, 23};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("arr["+ i +"]=" + arr[i]);
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 获取数组的长度语法
数组名.length
1
数组下标的范围是 0 至 数组长度-1 ,如果越界访问,就会报错。
// Array.java
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4
at com.array.Array.main(Array.java:15)
1
2
3
2
3
# 练习:
输出数组中的最大值、最小值和平均值
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个整型数组,并赋初值
int[] nums = new int[] { 61, 23, 4, 74, 13, 148, 20 };
int max = nums[0]; // 假定最大值为数组中的第一个元素
int min = nums[0]; // 假定最小值为数组中的第一个元素
double sum = 0;// 累加值
double avg = 0;// 平均值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 循环遍历数组中的元素
// 如果当前值大于max,则替换max的值
if (i > 0 && nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
// 如果当前值小于min,则替换min的值
if (i > 0 && nums[i] < min) {
min = nums[i];
}
// 累加求和
sum += nums[i];
}
// 求平均值
avg = sum / nums.length;
System.out.println("数组中的最大值:" + max);
System.out.println("数组中的最小值:" + min);
System.out.println("数组中的平均值:" + avg);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 使用 Arrays 类操作 Java 中的数组
Arrays 类是 Java 中提供的一个工具类,在 java.util 包中。该类中包含了一些方法用来直接操作数组,比如可直接实现数组的排序、搜索等
# 排序 sort()
// 语法:
Arrays.sort(数组名);
1
2
2
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个整型数组,并赋初值
int[] nums = new int[] { 61, 23, 4, 74, 13, 148, 20 };
Arrays.sort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后的首尾数为:" + nums[0] + ", " + nums[nums.length - 1]);
System.out.println("toString: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 将数组转换为字符串 toString()
// 语法:
Arrays.toString(数组名);
1
2
2
# foreach
foreach 并不是 Java 中的关键字,是 for 语句的特殊简化版本,在遍历数组、集合时, foreach 更简单便捷。
语法
for (元素类型 元素变量 : 遍历对象) { // do something }
for (int i : nums) {
System.out.println("print by foreach: " + i);
}
1
2
3
2
3
# 二维数组
声明数组/分配空间
数据类型[][] 数组名 = new 数据类型[行数][列数];
1
或
数据类型[][] 数组名;
数组名 = new 数据类型[行数][列数];
1
2
2
# CODE
Array.java
package com.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// right:
int score[] = new int[]{45, 56, 76, 23};
// error:
// Cannot define dimension expressions
// when an array initializer is provided
// int score[] = new int[4]{45, 56, 76, 23};
// error:
// Variable must provide either dimension expressions
// or an array initializer
// int[ ] score = new int[ ];
System.out.println(score[4]);
}
}
*/
/*
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个整型数组,并赋初值
int[] nums = new int[] { 61, 23, 4, 74, 13, 148, 20 };
int max = nums[0]; // 假定最大值为数组中的第一个元素
int min = nums[0]; // 假定最小值为数组中的第一个元素
double sum = 0;// 累加值
double avg = 0;// 平均值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 循环遍历数组中的元素
// 如果当前值大于max,则替换max的值
if (i > 0 && nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
// 如果当前值小于min,则替换min的值
if (i > 0 && nums[i] < min) {
min = nums[i];
}
// 累加求和
sum += nums[i];
}
// 求平均值
avg = sum / nums.length;
System.out.println("数组中的最大值:" + max);
System.out.println("数组中的最小值:" + min);
System.out.println("数组中的平均值:" + avg);
}
}
*/
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个整型数组,并赋初值
int[] nums = new int[] { 61, 23, 4, 74, 13, 148, 20 };
Arrays.sort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后的首尾数为:" + nums[0] + ", " + nums[nums.length - 1]);
System.out.println("toString: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
for (int i : nums) {
System.out.println("print by foreach: " + i);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
Test.java
package com.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* 创建指定长度的 int 型数组,
* 并生成 100 以内随机数为数组中的每个元素赋值,
* 然后输出数组
*/
//public class Test {
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test ts = new Test();
// // create array
// int[] arr = ts.createArray(8);
//
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
// }
//
// public int[] createArray(int length) {
// int[] arr = new int[length];
// for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// arr[i] = (int)(Math.random() * 100);
// }
// return arr;
// }
//}
/*
* 实现输出考试成绩的前三名
* 1、 考试成绩已保存在数组 scores 中,数组元素依次为 89 , -23 , 64 , 91 , 119 , 52 , 73
* 2、 要求通过自定义方法来实现成绩排名并输出操作,将成绩数组作为参数传入
* 3、 要求判断成绩的有效性( 0—100 ),如果成绩无效,则忽略此成绩
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test ts = new Test();
// create array
int[] scores = new int[]{89 , -23 , 64 , 91 , 119 , 52 , 73};
scores = ts.sort(scores);
// 输出0—100有效前3名成绩
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i ++) {
if (count >= 3) break;
if (scores[i] >= 0 && scores[i] <= 100) {
System.out.println(scores[i]);
count++;
}
}
}
/*
* 从大到小排序
*/
public int[] sort(int[] arr) {
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[i]) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67