# Collections工具类
java.util.Collections
1
是Java集合框架中,用来操作集合对象的工具类;也是Java集合框架的成员。
# Comparable和Comparator
Comparable: 默认比较规则;
Comparator: 临时比较规则;
Comparable和Comparator都是Java集合框架的成员。
# Comparable接口 —— 可比较的
实现该接口表示:这个类的实例可以比较大小,可以进行自然排序
定义了默认的比较规则
其实现类需要实现compareTo()方法
compareTo()方法返回正数表示大,负数表示小,0则表示相等。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 需求:
* 1、通过Collections.sort()方法,对Integer泛型的List进行排序;
* 2、对String泛型的List进行排序;
* 3、对其他类型泛型的List进行排序,以Student2为列
*/
public class TestCollection {
/**
* 1、通过Collections.sort()方法,对Integer泛型的List进行排序;
* 创建Integer泛型的List,插入10个100以内的不重复随机整数
* 调用Collections.sort()方法对其进行排序
*/
public void testSort1() {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 插入十个100以内的不重复随机整数
Random random = new Random();
Integer k;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
do {
k = random.nextInt(100);
} while (integerList.contains(k));
integerList.add(k);
System.out.println("成功添加整数:" + k);
}
System.out.println("------- before sort -------");
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder();
for (Integer integer : integerList) {
str1.append(integer + " ");
}
System.out.println(str1);
// 排序
System.out.println("------- after sort -------");
Collections.sort(integerList);
StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder();
for (Integer integer : integerList) {
str2.append(integer + " ");
}
System.out.println(str2);
}
/**
* 2、对String泛型的List进行排序;
* 创建String泛型的List,添加3个乱序的String元素
* 调用sort方法,再次输出排序后的顺序
*/
public void testSort2() {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("huawei");
stringList.add("alibaba");
stringList.add("jingdong");
System.out.println("------- before sort -------");
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder();
for (String str : stringList) {
str1.append(str + " ");
}
System.out.println(str1);
// 排序
System.out.println("------- after sort -------");
// string排序规则
// 0-9,A-Z,a-z
Collections.sort(stringList);
StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder();
for (String str : stringList) {
str2.append(str + " ");
}
System.out.println(str2);
}
/**
* 3、对其他类型泛型的List进行排序,以Student2为列
* Comparable和Comparator
*/
public void testSort3() {
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>();
Random random = new Random();
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Jack"));
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Maria"));
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Tomson"));
System.out.println("------- before sort -------");
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder();
for (Student st : studentList) {
str1.append(st.id + ":" + st.name + " ");
}
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println("------- after sort -------");
// 未实现Comparable接口前,会报以下错误:
// [WARNING:The method sort(List<T>) in the type Collections is not applicable for the arguments (List<Student>)]
Collections.sort(studentList);
StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder();
for (Student st : studentList) {
str2.append(st.id + ":" + st.name + " ");
}
System.out.println(str2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestCollection tc = new TestCollection();
tc.testSort1();
tc.testSort2();
tc.testSort3();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
Student类
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 学生类
* @author capricorncd
*
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
public int id;
public String name;
public Set<Course> courses;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (!(obj instanceof Student))
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
public Student (int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
// 初始化
this.courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// String
// return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
return this.id - o.id;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
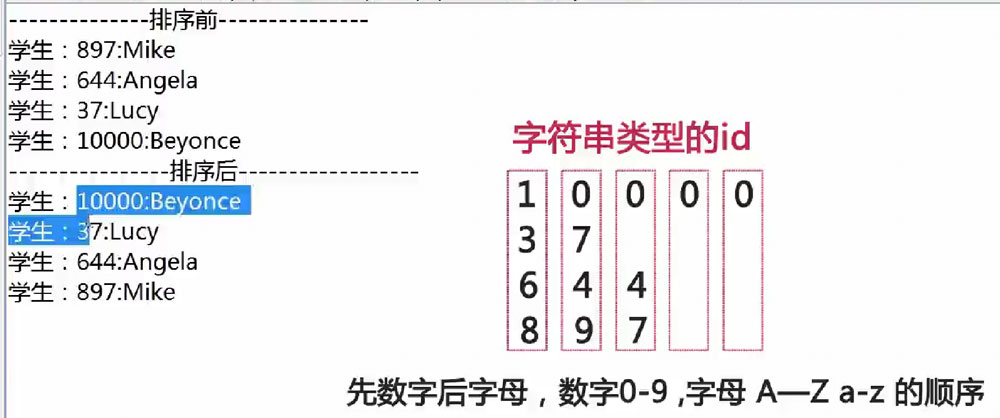
注意:当id为String类型时,其结果:
扩展练习
利用Collections.sort()方法,对泛型为String的List进行排序
创建完List
后,往其中添加10条随机字符串 ::: 每条字符串长度为10以内的随机整数 :::
每条字符串的每个字符都为随机生成的字符,字符可以重复 :::
每条随机字符串不可重复 :::
# Comparator接口 —— 比较工具接口
用户定义临时比较规则,而不是默认比较规则。
其实现类需要实现compare()方法。
可以将Comparator传递给sort方法(如Collections.sort或Arrays.sort)
package com.test.collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// 按学生姓名排序
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
改造TestCollection类testSrot3方法
/**
* 3、对其他类型泛型的List进行排序,以Student2为列
* Comparable和Comparator
*/
public void testSort3() {
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>();
Random random = new Random();
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Jack"));
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Maria"));
studentList.add(new Student(random.nextInt(1000), "Tomson"));
System.out.println("------- before sort -------");
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder();
for (Student st : studentList) {
str1.append(st.id + ":" + st.name + " ");
}
System.out.println(str1);
// id排序
System.out.println("------- after sort -------");
// 未实现Comparable接口前,会报以下错误:
// [WARNING:The method sort(List<T>) in the type Collections is not applicable for the arguments (List<Student>)]
Collections.sort(studentList);
StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder();
for (Student st : studentList) {
str2.append(st.id + ":" + st.name + " ");
}
System.out.println(str2);
// 姓名排序
System.out.println("------- sort by name -------");
Collections.sort(studentList, new StudentComparator());
StringBuilder str3 = new StringBuilder();
for (Student st : studentList) {
str3.append(st.id + ":" + st.name + " ");
}
System.out.println(str3);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
运行结果:
------- before sort -------
894:Jack 210:Maria 968:Tomson
------- after sort -------
210:Maria 894:Jack 968:Tomson
------- sort by name -------
894:Jack 210:Maria 968:Tomson
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6